As data is growing and businesses require rapid data analysis to make their decisions, a need emerged for systems that can support real-time analytics on streams of data with low latency. This article will show you how to spin up an Apache Pinot cluster in a simple way using Docker and docker-compose.
Apache Pinot is a real-time distributed OLAP datastore, built to deliver scalable real-time analytics with low latency on large datasets. It can ingest from batch data sources (such as Hadoop HDFS, Amazon S3, Azure ADLS, Google Cloud Storage) as well as stream data sources (such as Apache Kafka). Pinot is not only used to support complex analytics use cases, but also for anomaly detection and ad-hoc data exploration.
Pinot was built by engineers at LinkedIn and Uber and is using a columnar store, with several smart indexing and pre-aggregation techniques for low latency. Pinot also supports geospatial data analysis with the usage of Uber's H3 geoindexing. These features make Pinot a great choice for user-facing realtime analytics.
Pinot supports various integrations with other systems, some of which include Trino distributed query engine to support joins with other data sources, as well as Apache Superset for interactive dashboards.
Apache Pinot is availabe as a managed service from StarTree Cloud.
Pinot’s basic components
Apache Pinot’s basic components include the following:
Cluster
A Cluster is a set of nodes comprising of servers, brokers, controllers and minions.
Pinot uses Apache Helix for cluster management. Helix is a cluster management framework that manages replicated, partitioned resources in a distributed system. Helix uses Zookeeper to store cluster state and metadata.
Controller
The Pinot Controller is responsible for maintaining global metadata (e.g. configs and schemas) of the system with the help of Zookeeper which is used as the persistent metadata store. It hosts Apache Helix controller to manage all Pinot components, and, among other features, it maintainins the mapping of which servers are responsible for which segments. This mapping is used by the servers to download the portion of the segments that they are responsible for. This mapping is also used by the broker to decide which servers to route the queries to.
Broker
Pinot Brokers accept queries from clients and forwards the request to the appropriate servers. They gather all the responses from the servers and they unify them in a single response to the clients.
Server
Pinot Servers host the data segments and serve queries off the data they host. There are two types of servers, the offline and the real-time servers, to support both batch and real-time operations
Minion
Minion uses the Apache Helix Task Framework to offload computationally intensive tasks from other components.
Tenant
In order to support multi-tenancy among Pinot servers, Pinot has be configured class support for tenants. A table is associated with a tenant, which allows all tables belonging to a particular logical namespace to be grouped under a single tenant name and isolated from other tenants. This isolation between tenants provides different namespaces for applications and teams to prevent sharing tables or schemas.
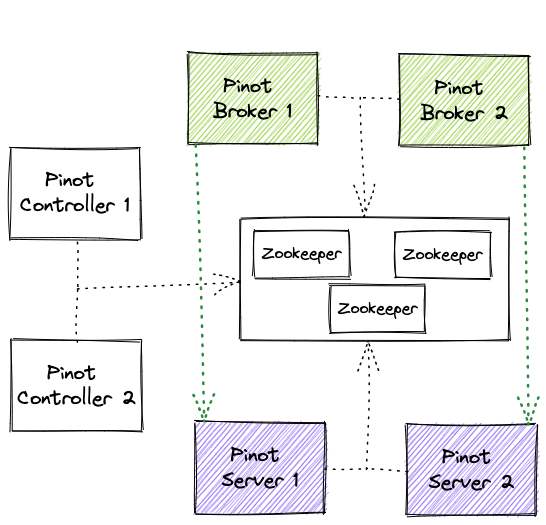
Fig. 1: Apache Pinot Architecture
Setup a cluster using Docker
To keep things simple, the current setup utilizes only the default tenant of Pinot, so, both Pinot servers belong to the DefaultTenant.
A cluster called PinotCluster (v0.10.0) will be created with the following components:
- 3 Zookeeper instances (ensemble)
- 2 Pinot Controllers
- 2 Pinot Brokers
- 2 Pinot Servers
It is important to keep this component starting sequence in order to form the cluster safely, thus, healthchecks have been configured to achieve this in Docker. In addition, Docker volumes are used to persist all data of the cluster.
# docker-compose.yml file
version: '3'
services:
zookeeper-1:
image: zookeeper:latest
hostname: zookeeper-1
restart: "unless-stopped"
ports:
- "2181:2181"
environment:
ZOO_MY_ID: 1
ZOO_PORT: 2181
ZOO_SERVERS: server.1=zookeeper-1:2888:3888;2181 server.2=zookeeper-2:2888:3888;2181 server.3=zookeeper-3:2888:3888;2181
volumes:
- zkData1:/data
- zkCatalog1:/catalog
healthcheck:
test: nc -z localhost 2181 || exit 1
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 10
zookeeper-2:
image: zookeeper:latest
restart: "unless-stopped"
hostname: zookeeper-2
ports:
- "2182:2181"
environment:
ZOO_MY_ID: 2
ZOO_PORT: 2181
ZOO_SERVERS: server.1=zookeeper-1:2888:3888;2181 server.2=zookeeper-2:2888:3888;2181 server.3=zookeeper-3:2888:3888;2181
volumes:
- zkData2:/data
- zkCatalog2:/catalog
healthcheck:
test: nc -z localhost 2181 || exit 1
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 10
zookeeper-3:
image: zookeeper:latest
restart: "unless-stopped"
hostname: zookeeper-3
ports:
- "2183:2181"
environment:
ZOO_MY_ID: 3
ZOO_PORT: 2181
ZOO_SERVERS: server.1=zookeeper-1:2888:3888;2181 server.2=zookeeper-2:2888:3888;2181 server.3=zookeeper-3:2888:3888;2181
volumes:
- zkData3:/data
- zkCatalog3:/catalog
healthcheck:
test: nc -z localhost 2181 || exit 1
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 10
controller-1:
image: apachepinot/pinot:0.10.0
restart: "unless-stopped"
hostname: controller-1
volumes:
- pinotController1:/tmp/data/controller
ports:
- "9001:9001"
command: StartController -zkAddress zookeeper-1:2181,zookeeper-2:2182,zookeeper-3:2183 -clusterName PinotCluster -controllerPort 9001
depends_on:
zookeeper-1:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-2:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-3:
condition: service_healthy
healthcheck:
test: curl --fail -s http://controller-1:9001/ || exit 1
interval: 1m30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 5
controller-2:
image: apachepinot/pinot:0.10.0
restart: "unless-stopped"
hostname: controller-2
volumes:
- pinotController2:/tmp/data/controller
ports:
- "9002:9002"
command: StartController -zkAddress zookeeper-1:2181,zookeeper-2:2182,zookeeper-3:2183 -clusterName PinotCluster -controllerPort 9002
depends_on:
zookeeper-1:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-2:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-3:
condition: service_healthy
controller-1:
condition: service_healthy
healthcheck:
test: curl --fail -s http://controller-2:9002/ || exit 1
interval: 1m30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 5
broker-1:
image: apachepinot/pinot:0.10.0
restart: "unless-stopped"
hostname: broker-1
ports:
- "7001:7001"
command: StartBroker -zkAddress zookeeper-1:2181,zookeeper-2:2182,zookeeper-3:2183 -clusterName PinotCluster -brokerPort 7001
depends_on:
zookeeper-1:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-2:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-3:
condition: service_healthy
controller-1:
condition: service_healthy
controller-2:
condition: service_healthy
broker-2:
image: apachepinot/pinot:0.10.0
restart: "unless-stopped"
hostname: broker-2
ports:
- "7002:7002"
command: StartBroker -zkAddress zookeeper-1:2181,zookeeper-2:2182,zookeeper-3:2183 -clusterName PinotCluster -brokerPort 7002
depends_on:
zookeeper-1:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-2:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-3:
condition: service_healthy
controller-1:
condition: service_healthy
controller-2:
condition: service_healthy
server-1:
image: apachepinot/pinot:0.10.0
restart: "unless-stopped"
hostname: server-1
volumes:
- pinotServer1:/tmp/data/server
ports:
- "8001:8001"
- "8011:8011"
command: StartServer -zkAddress zookeeper-1:2181,zookeeper-2:2182,zookeeper-3:2183 -clusterName PinotCluster -serverPort 8001 -serverAdminPort 8011
depends_on:
zookeeper-1:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-2:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-3:
condition: service_healthy
controller-1:
condition: service_healthy
controller-2:
condition: service_healthy
server-2:
image: apachepinot/pinot:0.10.0
restart: "unless-stopped"
hostname: server-2
volumes:
- pinotServer2:/tmp/data/server
ports:
- "8002:8002"
- "8012:8012"
command: StartServer -zkAddress zookeeper-1:2181,zookeeper-2:2182,zookeeper-3:2183 -clusterName PinotCluster -serverPort 8002 -serverAdminPort 8012
depends_on:
zookeeper-1:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-2:
condition: service_healthy
zookeeper-3:
condition: service_healthy
controller-1:
condition: service_healthy
controller-2:
condition: service_healthy
volumes:
zkData1:
zkData2:
zkData3:
zkCatalog1:
zkCatalog2:
zkCatalog3:
pinotController1:
pinotController2:
pinotServer1:
pinotServer2:
To start all services above, run the command:
docker-compose up -d
Navigate to localhost:9001 to check the Pinot cluster, its components and the query console. The memory consumption just to spin up the services is approximately 6GB and the time for all services to start is about 5-10 minutes (depending on the machine). It is highly recommended to use multiple machines to host the several containers of the cluster, as this setup is memory exhaustive to host in a single machine.
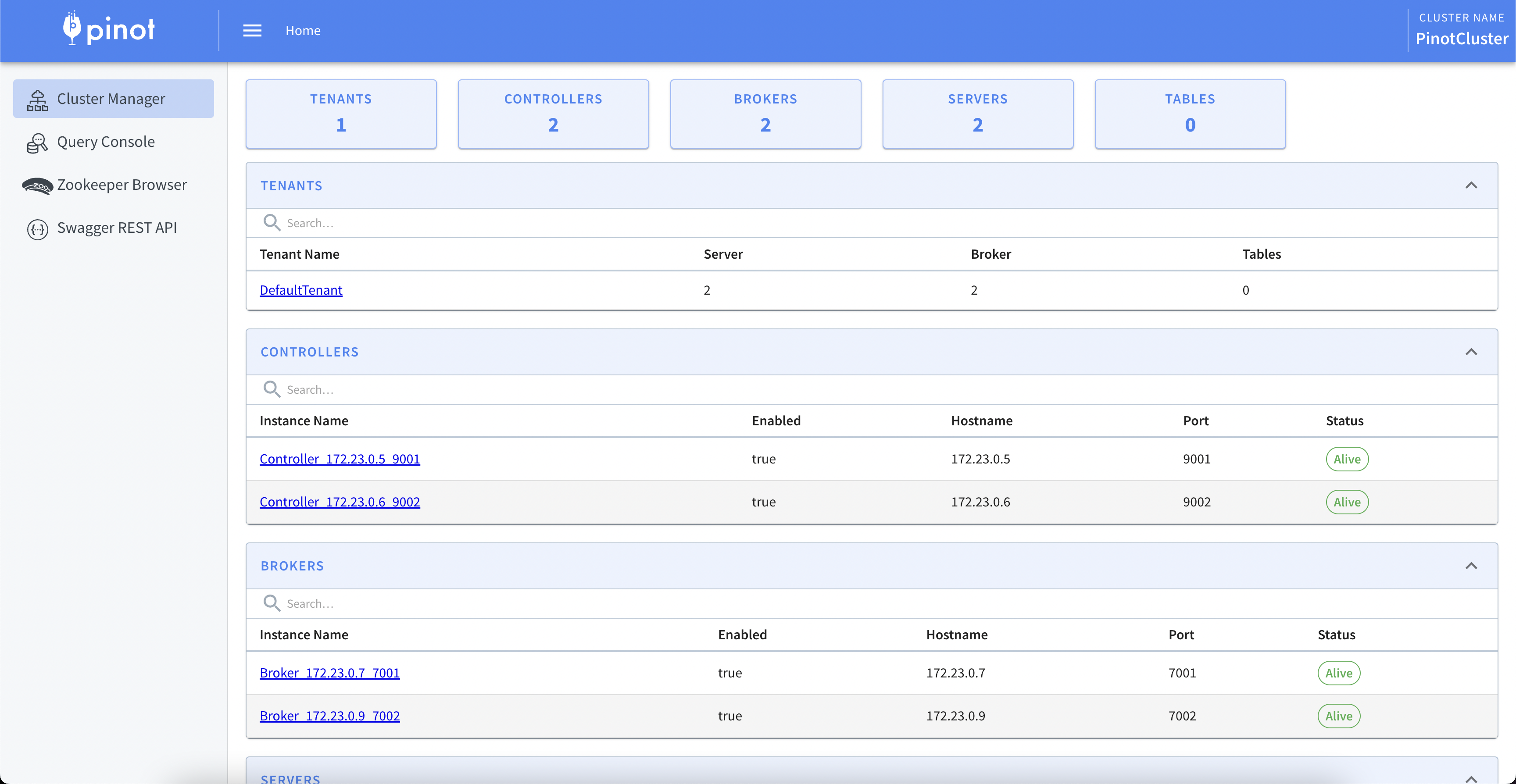
Fig. 2: Apache Pinot user interface
Ingest & query sample data in Apache Pinot
In order to test the cluster of Pinot, a simple CSV ingestion job will be executed using the following commands.
The CSV file to be ingested is a small dataset that contains songs. To speed up the ingestion, tracks schema file and table definition have been created. All associated files can be found in my GitHub repository.
# Create temp folders in the container
docker exec pinot-controller-1-1 mkdir -p /tmp/raw_data/tracks
docker exec pinot-controller-1-1 mkdir -p /tmp/definitions/
# Copy files to container
docker cp tracks.csv pinot-controller-1-1:/tmp/raw_data/tracks/
docker cp tracks-schema.json pinot-controller-1-1:/tmp/definitions/
docker cp tracks-table-offline.json pinot-controller-1-1:/tmp/definitions/
docker cp tracks_job_spec.yml pinot-controller-1-1:/tmp/definitions/
# Add schema and table
docker exec -it pinot-controller-1-1 \
/opt/pinot/bin/pinot-admin.sh AddTable \
-controllerPort 9001 \
-schemaFile /tmp/definitions/tracks-schema.json \
-tableConfigFile /tmp/definitions/tracks-table-offline.json \
-exec
# Ingest CSV data
docker exec -it pinot-controller-1-1 \
/opt/pinot/bin/pinot-admin.sh LaunchDataIngestionJob \
-jobSpecFile /tmp/definitions/tracks_job_spec.yml
Once the ingestion is completed, the table will be shown in the Cluster Manager view and can be queried using Pinot’s Query Console.
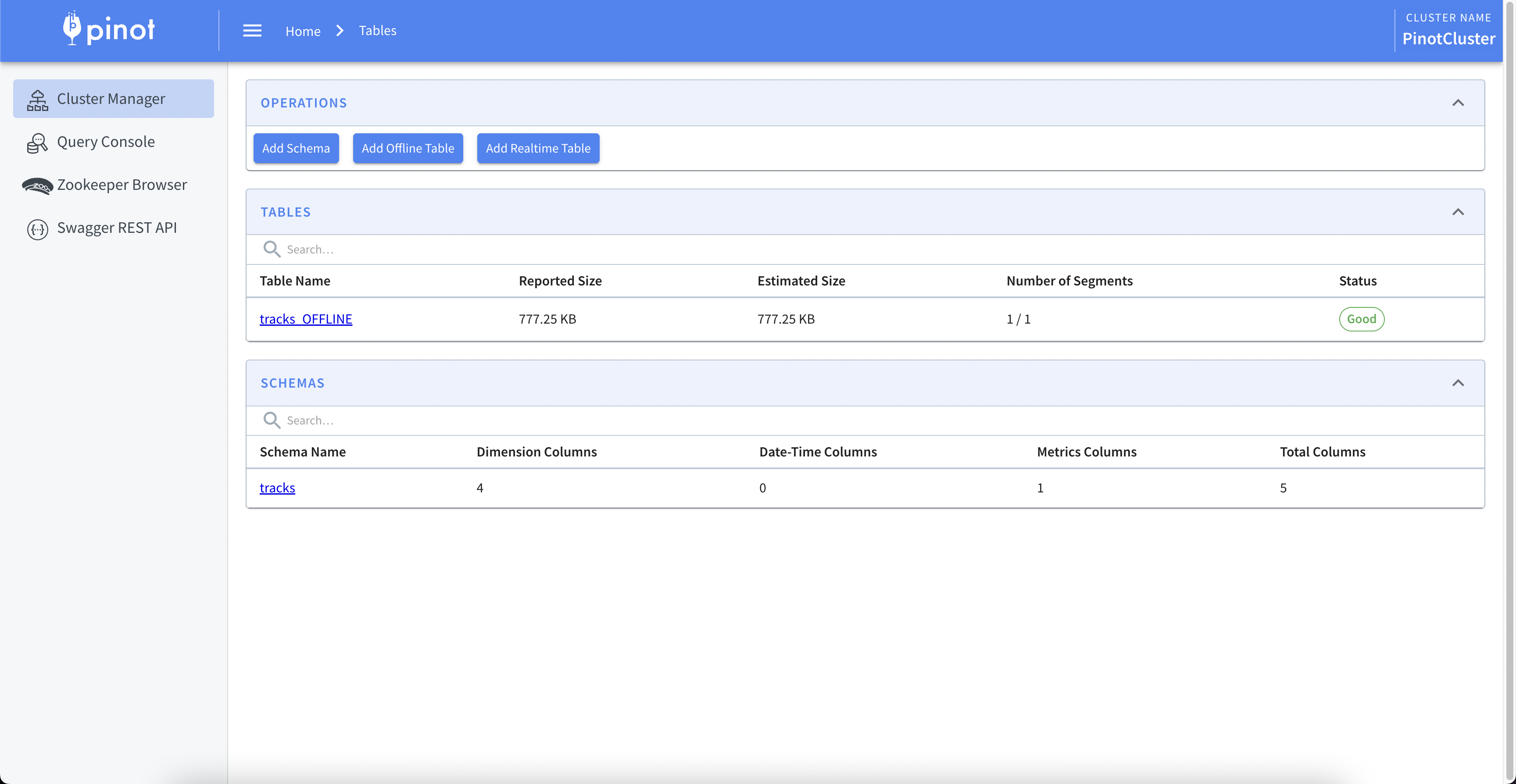
Fig. 3: Apache Pinot tables
A sample query to execute is:
SELECT
COUNT(*) AS num_of_songs, artist
FROM
tracks
GROUP BY
artist
ORDER BY
num_of_songs desc
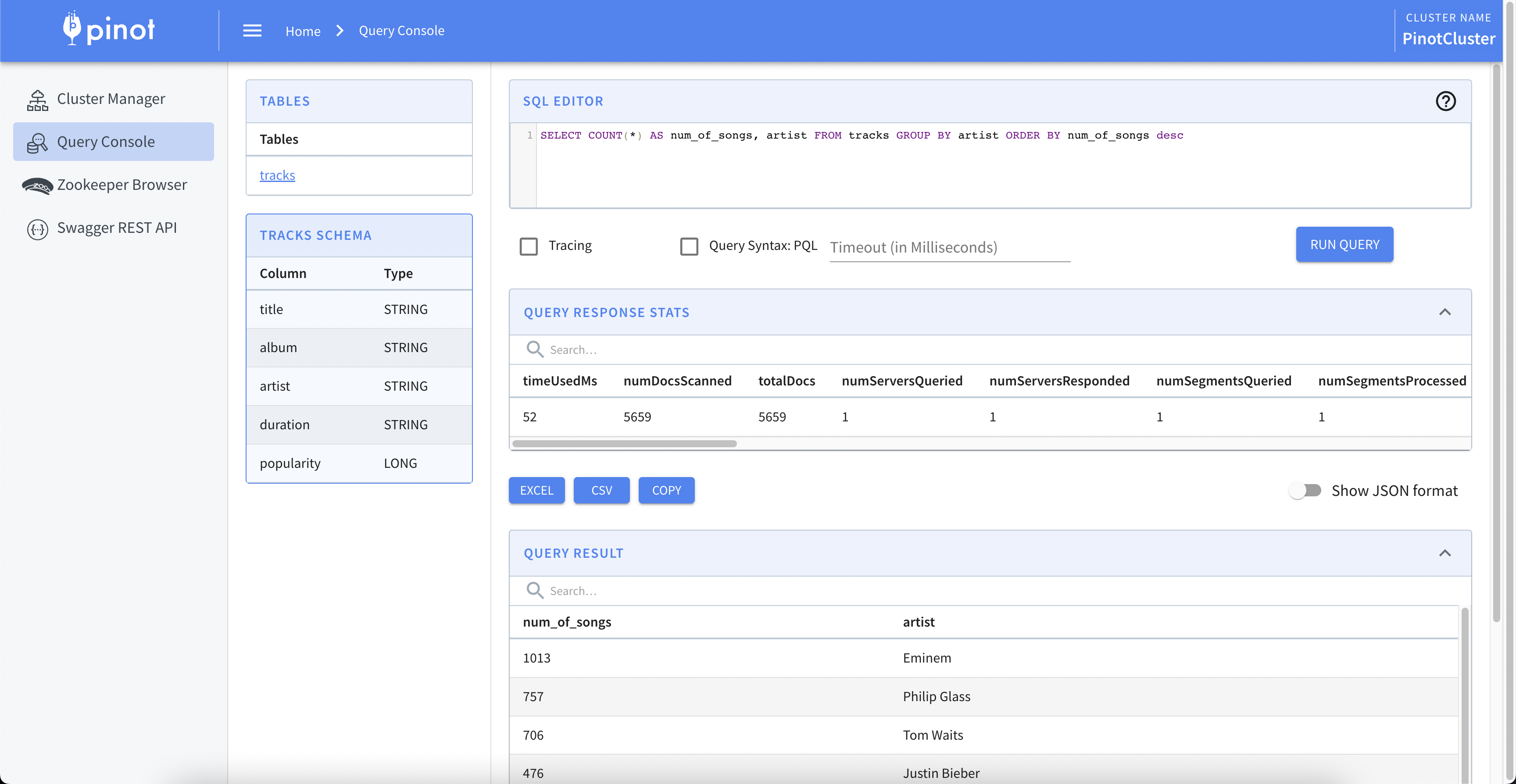
Fig. 4: Apache Pinot Query Console